Dig
Get DNS records for a domain.
- About dig
- Manual dig
- Statistics dig
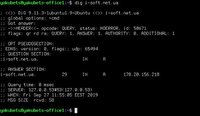
Dig (domain information groper) is a network administration command-line tool for querying the Domain Name System (DNS).
Dig is useful for network troubleshooting and for educational purposes. It can operate based on command line option and flag arguments, or in batch mode by reading requests from an operating system file. When a specific name server is not specified in the command invocation, it uses the operating system's default resolver, usually configured in the file resolv.conf. Without any arguments it queries the DNS root zone.
Dig supports Internationalized domain name (IDN) queries.
Dig is a component of the domain name server software suite BIND. dig supersedes in functionality older tools, such as nslookup and the program host; however, the older tools are still used in complementary fashion.
dig - DNS lookup utility
dig [@server] [-b address] [-c class] [-f filename] [-k filename] [-m] [-p port#] [-q name] [-t type] [-v] [-x addr] [-y [hmac:]name:key] [[-4] | [-6]] [name] [type] [class] [queryopt...]
dig [-h]
dig [global-queryopt...] [query...]
dig is a flexible tool for interrogating DNS name servers. It performs DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the name server(s) that were queried. Most DNS administrators use dig to troubleshoot DNS problems because of its flexibility, ease of use and clarity of output. Other lookup tools tend to have less functionality than dig.
Although dig is normally used with command-line arguments, it also has a batch mode of operation for reading lookup requests from a file. A brief summary of its command-line arguments and options is printed when the -h option is given. Unlike earlier versions, the BIND 9 implementation of dig allows multiple lookups to be issued from the command line.
Unless it is told to query a specific name server, dig will try each of the servers listed in /etc/resolv.conf. If no usable server addresses are found, dig will send the query to the local host.
When no command line arguments or options are given, dig will perform an NS query for "." (the root).
It is possible to set per-user defaults for dig via ${HOME}/.digrc. This file is read and any options in it are applied before the command line arguments.
The IN and CH class names overlap with the IN and CH top level domain names. Either use the -t and -c options to specify the type and class, use the -q the specify the domain name, or use "IN." and "CH." when looking up these top level domains.
A typical invocation of dig looks like:
dig @server name typewhere:
server
is the name or IP address of the name server to query. This can be an IPv4 address in dotted-decimal notation or an IPv6 address in colon-delimited notation. When the supplied server argument is a hostname, dig resolves that name before querying that name server. If no server argument is provided, dig consults /etc/resolv.conf; if an address is found there, it queries the name server at that address. If either of the -4 or -6 options are in use, then only addresses for the corresponding transport will be tried. If no usable addresses are found, dig will send the query to the local host. The reply from the name server that responds is displayed.
name
is the name of the resource record that is to be looked up.
type
indicates what type of query is required — ANY, A, MX, SIG, etc. type can be any valid query type. If no type argument is supplied, dig will perform a lookup for an A record.
-4 Use IPv4 only.
-6 Use IPv6 only.
-b address [#port] Set the source IP address of the query. The address must be a valid address on one of the host's network interfaces, or "0.0.0.0" or "::". An optional port may be specified by appending "#
-c class Set the query class. The default class is IN; other classes are HS for Hesiod records or CH for Chaosnet records.
-f file Batch mode: dig reads a list of lookup requests to process from the given file. Each line in the file should be organized in the same way they would be presented as queries to dig using the command-line interface.
-i Do reverse IPv6 lookups using the obsolete RFC1886 IP6.INT domain, which is no longer in use. Obsolete bit string label queries (RFC2874) are not attempted.
-k keyfile Sign queries using TSIG using a key read from the given file. Key files can be generated using tsig-keygen(8). When using TSIG authentication with dig, the name server that is queried needs to know the key and algorithm that is being used. In BIND, this is done by providing appropriate key and server statements in named.conf.
-m Enable memory usage debugging.
-p port Send the query to a non-standard port on the server, instead of the default port 53. This option would be used to test a name server that has been configured to listen for queries on a non-standard port number.
-q name The domain name to query. This is useful to distinguish the name from other arguments.
-t type The resource record type to query. It can be any valid query type which is supported in BIND 9. The default query type is "A", unless the -x option is supplied to indicate a reverse lookup. A zone transfer can be requested by specifying a type of AXFR. When an incremental zone transfer (IXFR) is required, set the type to ixfr=N. The incremental zone transfer will contain the changes made to the zone since the serial number in the zone's SOA record was N.
-u Print query times in microseconds instead of milliseconds.
-v Print the version number and exit.
-x addr Simplified reverse lookups, for mapping addresses to names. The addr is an IPv4 address in dotted-decimal notation, or a colon-delimited IPv6 address. When the -x is used, there is no need to provide the name, class and type arguments. dig automatically performs a lookup for a name like 94.2.0.192.in-addr.arpa and sets the query type and class to PTR and IN respectively. IPv6 addresses are looked up using nibble format under the IP6.ARPA domain (but see also the -i option).
-y [hmac:]keyname:secret Sign queries using TSIG with the given authentication key. keyname is the name of the key, and secret is the base64 encoded shared secret. hmac is the name of the key algorithm; valid choices are hmac-md5, hmac-sha1, hmac-sha224, hmac-sha256, hmac-sha384, or hmac-sha512. If hmac is not specified, the default is hmac-md5 or if MD5 was disabled hmac-sha256.
NOTE: You should use the -k option and avoid the -y option, because with -y the shared secret is supplied as a command line argument in clear text. This may be visible in the output from ps(1) or in a history file maintained by the user's shell.
dig provides a number of query options which affect the way in which lookups are made and the results displayed. Some of these set or reset flag bits in the query header, some determine which sections of the answer get printed, and others determine the timeout and retry strategies.
Each query option is identified by a keyword preceded by a plus sign (+). Some keywords set or reset an option. These may be preceded by the string no to negate the meaning of that keyword. Other keywords assign values to options like the timeout interval. They have the form +keyword=value. Keywords may be abbreviated, provided the abbreviation is unambiguous; for example, +cd is equivalent to +cdflag. The query options are:
- +[no]aaflag
- A synonym for +[no]aaonly.
- +[no]aaonly
- Sets the "aa" flag in the query.
- +[no]additional
- Display [do not display] the additional section of a reply. The default is to display it.
- +[no]adflag
- Set [do not set] the AD (authentic data) bit in the query. This requests the server to return whether all of the answer and authority sections have all been validated as secure according to the security policy of the server. AD=1 indicates that all records have been validated as secure and the answer is not from a OPT-OUT range. AD=0 indicate that some part of the answer was insecure or not validated. This bit is set by default.
- +[no]all
- et or clear all display flags.
- +[no]answer
- Display [do not display] the answer section of a reply. The default is to display it.
- +[no]authority
- Display [do not display] the authority section of a reply. The default is to display it.
- +[no]badcookie
- Retry lookup with the new server cookie if a BADCOOKIE response is received.
- +[no]besteffort
- Attempt to display the contents of messages which are malformed. The default is to not display malformed answers.
- +bufsize=B
- Set the UDP message buffer size advertised using EDNS0 to B bytes. The maximum and minimum sizes of this buffer are 65535 and 0 respectively. Values outside this range are rounded up or down appropriately. Values other than zero will cause a EDNS query to be sent.
- +[no]cdflag
- Set [do not set] the CD (checking disabled) bit in the query. This requests the server to not perform DNSSEC validation of responses.
- +[no]class
- Display [do not display] the CLASS when printing the record.
- +[no]cmd
- Toggles the printing of the initial comment in the output identifying the version of dig and the query options that have been applied. This comment is printed by default.
- +[no]comments
- Toggle the display of comment lines in the output. The default is to print comments.
- +[no]cookie[=####]
- Send a COOKIE EDNS option, with optional value. Replaying a COOKIE from a previous response will allow the server to identify a previous client. The default is +cookie.
- +cookie is also set when +trace is set to better emulate the default queries from a nameserver.
- +[no]crypto
- Toggle the display of cryptographic fields in DNSSEC records. The contents of these field are unnecessary to debug most DNSSEC validation failures and removing them makes it easier to see the common failures. The default is to display the fields. When omitted they are replaced by the string "[omitted]" or in the DNSKEY case the key id is displayed as the replacement, e.g. "[ key id = value ]".
- +[no]defname
- Deprecated, treated as a synonym for +[no]search.
- +[no]dnssec
- Requests DNSSEC records be sent by setting the DNSSEC OK bit (DO) in the OPT record in the additional section of the query.
- +domain=somename
- Set the search list to contain the single domain somename, as if specified in a domain directive in /etc/resolv.conf, and enable search list processing as if the +search option were given.
- +dscp=value
- Set the DSCP code point to be used when sending the query. Valid DSCP code points are in the range [0..63]. By default no code point is explicitly set.
- +[no]edns[=#]
- Specify the EDNS version to query with. Valid values are 0 to 255. Setting the EDNS version will cause a EDNS query to be sent. +noedns clears the remembered EDNS version. EDNS is set to 0 by default.
- +[no]ednsflags[=#]
- Set the must-be-zero EDNS flags bits (Z bits) to the specified value. Decimal, hex and octal encodings are accepted. Setting a named flag (e.g. DO) will silently be ignored. By default, no Z bits are set.
- +[no]ednsnegotiation
- Enable/disable EDNS version negotiation. By default EDNS version negotiation is enabled.
- +[no]ednsopt[=code[:value]]
- Specify EDNS option with code point code and optionally payload of value as a hexadecimal string. code can be either an EDNS option name (for example, NSID or ECS), or an arbitrary numeric value. +noednsopt clears the EDNS options to be sent.
- +[no]expire
- Send an EDNS Expire option.
- +[no]fail
- Do not try the next server if you receive a SERVFAIL. The default is to not try the next server which is the reverse of normal stub resolver behavior.
- +[no]header-only
- Send a query with a DNS header without a question section. The default is to add a question section. The query type and query name are ignored when this is set.
- +[no]identify
- Show [or do not show] the IP address and port number that supplied the answer when the +short option is enabled. If short form answers are requested, the default is not to show the source address and port number of the server that provided the answer.
- +[no]idnout
- Convert [do not convert] puny code on output. This requires IDN SUPPORT to have been enabled at compile time. The default is to convert output.
- +[no]ignore
- Ignore truncation in UDP responses instead of retrying with TCP. By default, TCP retries are performed.
- +[no]keepopen
- Keep the TCP socket open between queries and reuse it rather than creating a new TCP socket for each lookup. The default is +nokeepopen.
- +[no]mapped
- Allow mapped IPv4 over IPv6 addresses to be used. The default is +mapped.
- +[no]multiline
- Print records like the SOA records in a verbose multi-line format with human-readable comments. The default is to print each record on a single line, to facilitate machine parsing of the dig output.
- +ndots=D
- Set the number of dots that have to appear in name to D for it to be considered absolute. The default value is that defined using the ndots statement in /etc/resolv.conf, or 1 if no ndots statement is present. Names with fewer dots are interpreted as relative names and will be searched for in the domains listed in the search or domain directive in /etc/resolv.conf if +search is set.
- +[no]nsid
- Include an EDNS name server ID request when sending a query.
- +[no]nssearch
- When this option is set, dig attempts to find the authoritative name servers for the zone containing the name being looked up and display the SOA record that each name server has for the zone.
- +[no]onesoa
- Print only one (starting) SOA record when performing an AXFR. The default is to print both the starting and ending SOA records.
- +[no]opcode=value
- Set [restore] the DNS message opcode to the specified value. The default value is QUERY (0).
- +[no]qr
- Print [do not print] the query as it is sent. By default, the query is not printed.
- +[no]question
- Print [do not print] the question section of a query when an answer is returned. The default is to print the question section as a comment.
- +[no]rdflag
- A synonym for +[no]recurse.
- +[no]recurse
- Toggle the setting of the RD (recursion desired) bit in the query. This bit is set by default, which means dig normally sends recursive queries. Recursion is automatically disabled when the +nssearch or +trace query options are used.
- +retry=T
- Sets the number of times to retry UDP queries to server to T instead of the default, 2. Unlike +tries, this does not include the initial query.
- +[no]rrcomments
- Toggle the display of per-record comments in the output (for example, human-readable key information about DNSKEY records). The default is not to print record comments unless multiline mode is active.
- +[no]search
- Use [do not use] the search list defined by the searchlist or domain directive in resolv.conf (if any). The search list is not used by default. 'ndots' from resolv.conf (default 1) which may be overridden by +ndots determines if the name will be treated as relative or not and hence whether a search is eventually performed or not.
- +[no]short
- Provide a terse answer. The default is to print the answer in a verbose form.
- +[no]showsearch
- Perform [do not perform] a search showing intermediate results.
- +[no]sigchase
- Chase DNSSEC signature chains. Requires dig be compiled with -DDIG_SIGCHASE. This feature is deprecated. Use delv instead.
- +split=W
- Split long hex- or base64-formatted fields in resource records into chunks of W characters (where W is rounded up to the nearest multiple of 4). +nosplit or +split=0 causes fields not to be split at all. The default is 56 characters, or 44 characters when multiline mode is active.
- +[no]stats
- This query option toggles the printing of statistics: when the query was made, the size of the reply and so on. The default behavior is to print the query statistics.
- +[no]subnet=addr[/prefix-length]
- Send (don't send) an EDNS Client Subnet option with the specified IP address or network prefix. dig +subnet=0.0.0.0/0, or simply dig +subnet=0 for short, sends an EDNS CLIENT-SUBNET option with an empty address and a source prefix-length of zero, which signals a resolver that the client's address information must not be used when resolving this query.
- +[no]tcp
- Use [do not use] TCP when querying name servers. The default behavior is to use UDP unless a type any or ixfr=N query is requested, in which case the default is TCP. AXFR queries always use TCP.
- +timeout=T
- Sets the timeout for a query to T seconds. The default timeout is 5 seconds. An attempt to set T to less than 1 will result in a query timeout of 1 second being applied.
- +[no]topdown
- When chasing DNSSEC signature chains perform a top-down validation. Requires dig be compiled with -DDIG_SIGCHASE. This feature is deprecated. Use delv instead.
- +[no]trace
- Toggle tracing of the delegation path from the root name servers for the name being looked up. Tracing is disabled by default. When tracing is enabled, dig makes iterative queries to resolve the name being looked up. It will follow referrals from the root servers, showing the answer from each server that was used to resolve the lookup.
If @server is also specified, it affects only the initial query for the root zone name servers.
+dnssec is also set when +trace is set to better emulate the default queries from a nameserver.
- Toggle tracing of the delegation path from the root name servers for the name being looked up. Tracing is disabled by default. When tracing is enabled, dig makes iterative queries to resolve the name being looked up. It will follow referrals from the root servers, showing the answer from each server that was used to resolve the lookup.
- +tries=T
- Sets the number of times to try UDP queries to server to T instead of the default, 3. If T is less than or equal to zero, the number of tries is silently rounded up to 1.
- +trusted-key=####
- Specifies a file containing trusted keys to be used with +sigchase. Each DNSKEY record must be on its own line.
If not specified, dig will look for /etc/trusted-key.key then trusted-key.key in the current directory.
Requires dig be compiled with -DDIG_SIGCHASE. This feature is deprecated. Use delv instead.
- Specifies a file containing trusted keys to be used with +sigchase. Each DNSKEY record must be on its own line.
- +[no]ttlid
- Display [do not display] the TTL when printing the record.
- +[no]ttlunits
- Display [do not display] the TTL in friendly human-readable time units of "s", "m", "h", "d", and "w", representing seconds, minutes, hours, days and weeks. Implies +ttlid.
- +[no]unknownformat
- Print all RDATA in unknown RR type presentation format (RFC 3597). The default is to print RDATA for known types in the type's presentation format.
- +[no]vc
- Use [do not use] TCP when querying name servers. This alternate syntax to +[no]tcp is provided for backwards compatibility. The "vc" stands for "virtual circuit"
- +[no]zflag
- Set [do not set] the last unassigned DNS header flag in a DNS query. This flag is off by default.
The BIND 9 implementation of dig supports specifying multiple queries on the command line (in addition to supporting the -f batch file option). Each of those queries can be supplied with its own set of flags, options and query options.
In this case, each query argument represent an individual query in the command-line syntax described above. Each consists of any of the standard options and flags, the name to be looked up, an optional query type and class and any query options that should be applied to that query.
A global set of query options, which should be applied to all queries, can also be supplied. These global query options must precede the first tuple of name, class, type, options, flags, and query options supplied on the command line. Any global query options (except the +[no]cmd option) can be overridden by a query-specific set of query options. For example:
dig +qr www.isc.org any -x 127.0.0.1 isc.org ns +noqr
shows how dig could be used from the command line to make three lookups: an ANY query for www.isc.org, a reverse lookup of 127.0.0.1 and a query for the NS records of isc.org. A global query option of +qr is applied, so that dig shows the initial query it made for each lookup. The final query has a local query option of +noqr which means that dig will not print the initial query when it looks up the NS records for isc.org.
/etc/resolv.conf
${HOME}/.digrc
delv(1), host(1), named(8), dnssec-keygen(8), RFC1035.
There are probably too many query options.
Internet Systems Consortium, Inc.
Copyright © 2000-2011, 2013-2018 Internet Systems Consortium, Inc. ("ISC")
ISC 2014-02-19 DIG(1)
| Date | Quantity |
|---|---|
| February 1, 2026 | 1 |
| January 29, 2026 | 1 |
| January 25, 2026 | 1 |
| November 21, 2025 | 4 |
| November 4, 2025 | 1 |
| November 3, 2025 | 1 |
| July 29, 2025 | 1 |
| April 27, 2025 | 2 |
| January 29, 2025 | 871 |
| September 11, 2024 | 1 |
| 884 |